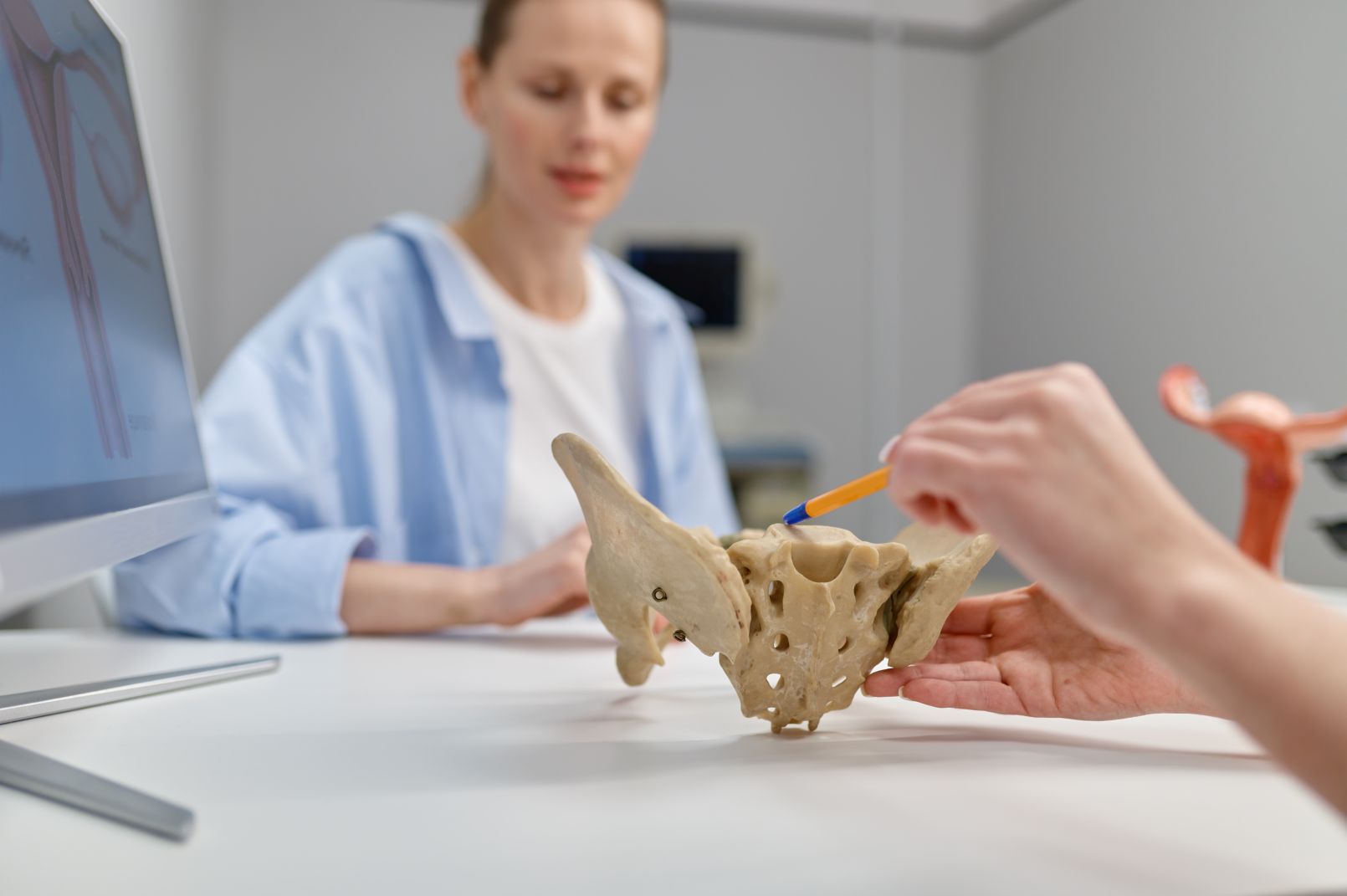
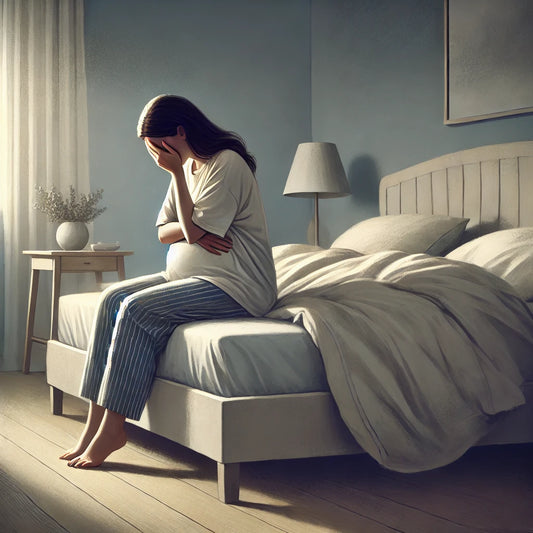
Vaginismus is a medical condition that can affect women, impacting their sexual well-being. It is characterized by involuntary contractions of the muscles surrounding the vagina, which can lead to painful sexual intercourse or difficulty inserting objects into the vagina. In this blog post, we will delve deeper into vaginismus, including its causes, how to recognize it, and the available treatment options.
What Causes Vaginismus?
-
Psychological Factors: Vaginismus can be triggered by emotional factors such as anxiety, stress, traumatic experiences, or negative thoughts about sexuality. These emotions can lead to unconscious muscle tension during attempts at penetration.
-
Physical Causes: Sometimes, vaginismus may be associated with physical conditions like infections, inflammations, scars, or congenital abnormalities in the genital area. These issues can increase muscle tension, resulting in vaginal pain.
Symptoms of Vaginismus:
Symptoms of vaginismus vary in severity and can include:
- Pain during attempts at sexual intercourse.
- Inability to insert tampons.
- Anxiety related to sexual activity.
- Difficulty with gynecological examinations.
Treating Vaginismus:
Fortunately, vaginismus is treatable, and several approaches are available:
-
Physical Therapy: Physical therapists specializing in pelvic floor rehabilitation can teach techniques to relax muscles and improve control over pelvic floor muscles.
-
Psychotherapy: Sexual therapy or counseling can help women understand and address emotional factors contributing to vaginismus.
-
Medication: In some cases, medications like muscle relaxants may be prescribed to reduce muscle tension.
-
Exercises: Kegel exercises and other pelvic floor exercises can be beneficial in reducing muscle tension and enhancing control.
-
Sexual Aids: The use of lubricants or vaginal dilators can aid in gently stretching vaginal muscles.
Remember that the treatment for vaginismus is tailored to the individual's specific cause and symptoms. If you suspect you are experiencing vaginismus, it is advisable to seek professional advice from a doctor, gynecologist, or sex therapist. The key is to engage in open and honest discussions about this topic and seek help to improve your sexual health and overall well-being.